This nation is in Vacation Mode for the next 1,452 turns. This nation cannot be attacked or traded with during that time.
| National Factbook |
| Flag: |
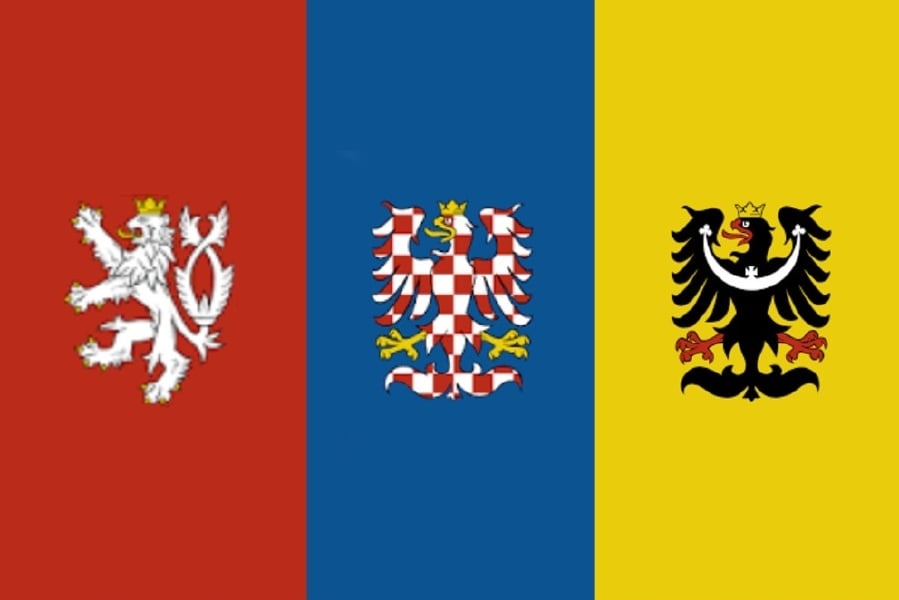

|
| Nation Name: |
The Union of Czech States |
| Leader Name: |
Petr Pavel |
| Currency: |

Czech Koruna (CZK) |
| National Animal: |

Lion |
| History: |
The roots of the Czech nation can be traced back to the arrival of Slavic tribes in the region of Bohemia during the 6th century. In the 9th century, the territory came under the rule of the Great Moravian Empire. However, it was during the reign of Duke Bořivoj and his successor, Saint Wenceslas, in the 10th century that the Czech state began to take shape.
The Bohemian Duchy, centered around Prague, emerged as a significant power under the rule of the Přemyslid dynasty. This period witnessed the spread of Christianity, with Saint Wenceslas becoming a symbol of Czech statehood. The reign of King Charles IV in the 14th century was a golden age, as Prague became a center of culture, education, and commerce, earning the title of the "Golden City."
In the 15th century, religious tensions and political conflicts led to the Hussite Wars. Jan Hus, a Czech religious reformer, played a crucial role in sparking a movement that challenged the Catholic Church. The Hussite armies successfully resisted several crusades and negotiated their religious freedoms in the 15th-century Hussite Compact.
The Czech lands came under the Habsburg monarchy in the 16th century after the defeat of the Bohemian Estates in the Battle of White Mountain during the Thirty Years' War. The Habsburg rule brought about a period of Germanization and suppression of Czech language and culture, leading to resistance and Czech national revival movements.
The 19th century saw the rise of Czech nationalism and a cultural revival, known as the Czech National Revival. Prominent figures such as Jan Amos Comenius, František Palacký, and Bedřich Smetana played key roles in promoting Czech language, literature, and music. The Austro-Hungarian Empire granted some concessions to Czech aspirations, including the establishment of Czech universities and increased autonomy.
The aftermath of World War I led to the creation of Czechoslovakia in 1918, a new nation that encompassed Czechs, Slovaks, and other ethnic groups. Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk became the first president, and Czechoslovakia became a prosperous and democratic state. The interwar period witnessed cultural and economic growth, but political tensions between Czechs and Germans persisted.
Tragically, Czechoslovakia was dismembered by Nazi Germany in 1938-1939, and subsequently occupied during World War II. The Czech resistance movement fought against the Nazi regime, and the assassination of Reinhard Heydrich by Czechoslovak parachutists in 1942 remains a significant act of resistance.
After the war, Czechoslovakia was restored, but the country fell under communist rule following a coup in 1948. The communist era, marked by repression and the Soviet influence, lasted until the Velvet Revolution of 1989. Led by Václav Havel and other dissidents, the peaceful revolution brought democracy back to Czechoslovakia.
In 1993, Czechoslovakia peacefully split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia, becoming independent nations. The Czech Republic experienced a transition to a market economy and integration into Western institutions like the European Union and NATO.
Today, the Czech Republic is a thriving and prosperous country, known for its rich cultural heritage, picturesque towns, and contributions to fields such as literature, music, and film. The Czechs have come a long way from their Slavic origins, overcoming numerous challenges to build a democratic nation that celebrates its history while embracing the opportunities of the future. |
| Geography |
| Continent: |
Europe |
| Land Area: |
64,373.60 sq. km |
| Terrain: |
The Czech terrain is a diverse landscape that encapsulates both natural beauty and historical charm. Situated in Central Europe, the Czech Republic boasts an array of geographical features that make it a captivating destination.
The country is predominantly characterized by rolling lowlands and highlands, with the Carpathian Mountains dominating the eastern border. The western part is adorned with the Bohemian Massif, which encompasses the Bohemian Forest, Ore Mountains, and Krkonoše, the highest range in the country. These mountains offer breathtaking vistas, scenic hiking trails, and winter sports opportunities.
Interlaced throughout the countryside are picturesque river valleys, the most significant being the Vltava and the Elbe, which flow through Prague, the capital city. These rivers meander across fertile plains, providing stunning landscapes and opportunities for water activities like boating and fishing.
In addition to its natural features, the Czech Republic is renowned for its captivating karst landscapes. The Moravian Karst, located in the southeast, is a mesmerizing labyrinth of underground caverns, gorges, and limestone formations. Among its notable attractions is the Punkva Caves, featuring an underground river and the awe-inspiring Macocha Abyss.
The country also boasts a plethora of enchanting forests, such as the Bohemian Paradise and Šumava National Park. These dense woodlands are home to diverse flora and fauna, making them an ideal destination for nature lovers and outdoor enthusiasts.
Adding to the charm of the Czech terrain are the countless historical towns and architectural gems scattered across the countryside. The UNESCO World Heritage Sites of Český Krumlov, Telč, and Kutná Hora are prime examples of the country's rich history and cultural heritage. These towns showcase stunning medieval castles, well-preserved historic centers, and intricate baroque and Gothic architecture.
Furthermore, the Czech Republic is famous for its spa towns, known for their healing mineral springs. Karlovy Vary and Mariánské Lázně are two prominent examples where visitors can relax in grand spa resorts and partake in wellness treatments.
In summary, the Czech terrain offers a blend of natural wonders, including mountains, valleys, rivers, and karst formations. The captivating landscapes are complemented by historical towns, architectural treasures, and rejuvenating spa towns. Whether exploring the rugged outdoors or immersing oneself in the country's cultural heritage, the Czech Republic presents a captivating tapestry of terrain that appeals to a wide range of visitors. |
| Highest Peak: |
Sněžka, 1,603 meters |
| Lowest Valley: |
Hřensko, 115 meters |
| Climate: |
The Czech Republic experiences a temperate continental climate, characterized by distinct seasons and moderate rainfall throughout the year. The climate is influenced by its inland location in Central Europe, with minimal influence from surrounding bodies of water.
Spring (March to May) brings the awakening of nature after the winter months. Temperatures gradually rise, starting with cooler weather in March and transitioning to milder conditions in May. Spring is a pleasant time to visit the Czech Republic, with blooming flowers and lush greenery creating a picturesque atmosphere.
Summer (June to August) is the warmest season in the Czech Republic. Average temperatures range between 20°C (68°F) and 30°C (86°F), although occasional heatwaves can result in temperatures exceeding 35°C (95°F). Summers are generally sunny and humid, particularly in July and August. This period sees an influx of tourists, attracted by the pleasant weather and numerous outdoor festivals and events.
Autumn (September to November) is a beautiful season characterized by colorful foliage and mild temperatures. September and October are generally mild and pleasant, making it an ideal time for hiking and exploring the countryside. However, as autumn progresses, temperatures gradually cool down, and November often brings the first snowfall, especially in higher elevations.
Winter (December to February) in the Czech Republic is cold and snowy, particularly in the mountainous regions. Temperatures range from around freezing point to -5°C (23°F), with occasional dips below -10°C (14°F). Snow covers the landscape, creating a picturesque winter wonderland. Skiing, snowboarding, and other winter sports are popular activities in the Czech Republic during this season.
Rainfall in the Czech Republic is relatively evenly distributed throughout the year, with slightly higher precipitation in summer. The country receives an average of 500 to 800 millimeters (20 to 31 inches) of rainfall annually, which nourishes the lush countryside and contributes to the country's greenery.
Weather patterns in the Czech Republic can be variable, with occasional fluctuations and rapid changes. It is advisable to pack appropriate clothing for layering and be prepared for sudden weather shifts, especially during transitional seasons.
Overall, the Czech Republic's climate offers a pleasant mix of seasons, allowing visitors to experience the beauty of nature throughout the year. From the vibrant blooms of spring to the warm and sunny summers, the colorful autumns, and the snowy landscapes of winter, each season has its own unique charm, providing a diverse range of experiences for travelers. |
| People & Society |
| Population: |
2,255,069 people |
| Demonym: |
Czech |
| Demonym Plural: |
Czech |
| Ethnic Groups: |
Czech - 89.0%
Moravian - 3.3%
Slovak - 0.9% |
| Languages: |
Czech - 98.7%
English - 11.7%
German - 8.6% |
| Religions: |
Atheism - 100.0% |
| Health |
| Life Expectancy: |
79 years |
| Obesity: |
6% |
| Alcohol Users: |
87.9% |
| Tobacco Users: |
0% |
| Cannabis Users: |
3% |
| Hard Drug Users: |
0% |
| Economy |
| Description: |
The Czech Republic has a highly industrialized and export-oriented economy. It benefits from a well-educated and skilled workforce, a strategic central location in Europe, and a stable business environment. The country has embraced economic liberalization, privatization, and market-oriented reforms, leading to robust economic growth and attracting foreign investment.
The industrial sector is a key pillar of the Czech economy. It encompasses various industries such as automotive manufacturing, machinery, electrical engineering, and chemicals. Prominent Czech companies, including Škoda Auto, a subsidiary of Volkswagen Group, play a vital role in the automotive sector. The country has become a major automobile producer and exporter in the region.
The Czech Republic has a strong tradition of engineering and innovation, with a focus on advanced manufacturing and technology. This has fostered a favorable environment for research and development activities. The country has several world-class research institutions and universities that contribute to technological advancements and innovation.
The services sector is another crucial component of the Czech economy. It includes finance, information technology, tourism, and business services. Prague, the capital city, is a significant financial hub and attracts international companies seeking a Central European base. The tourism industry has experienced growth, with visitors drawn to the country's rich cultural heritage, historic architecture, and picturesque landscapes.
Trade plays a vital role in the Czech economy. The country is highly integrated into global markets and has a strong export orientation. Major trading partners include Germany, Slovakia, Poland, and other European Union (EU) member states. Machinery, automobiles, electronics, and chemicals are among the top export goods.
Membership in the EU has been beneficial for the Czech Republic, providing access to a large single market and financial support for infrastructure development. The country adopted the Czech koruna (CZK) as its currency but has yet to adopt the Euro.
The government has pursued fiscal responsibility, resulting in relatively low public debt and a stable financial system. The Czech National Bank has maintained a prudent monetary policy, targeting inflation and promoting price stability. Foreign direct investment has flowed into the country due to favorable conditions, including a skilled labor force, a well-developed infrastructure, and a business-friendly regulatory framework.
Challenges facing the Czech economy include demographic issues such as an aging population and a declining birth rate. The country needs to address these challenges to sustain long-term economic growth. Additionally, maintaining competitiveness in a globalized market, investing in innovation and research, and addressing regional disparities are important areas for further development.
In summary, the Czech economy is a thriving market-oriented economy driven by a strong industrial base, innovation, and international trade. It benefits from a skilled workforce, a favorable business environment, and EU membership. Continued focus on technological advancements, human capital development, and addressing demographic challenges will be vital for future economic success. |
| Average Yearly Income: |
$60.42 |
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP): |
$1,055,199,294.00 |
| GDP per Capita: |
$467.92 |
| Gross National Income (GNI): |
$337,478,270.00 |
| Industries: |
The automotive industry is one of the key drivers of the Czech industrial sector. The country has a long-standing tradition of automotive manufacturing, and it has attracted significant foreign direct investment from renowned global automotive companies. The production of automobiles and automotive components is a major contributor to the Czech economy. Companies such as Škoda Auto, a subsidiary of Volkswagen Group, have a strong presence in the country and are known for their high-quality vehicles. The automotive sector contributes significantly to exports, job creation, and technological advancements in the Czech Republic.
Machinery and engineering form another vital segment of the Czech industry. The country has a strong engineering tradition, and Czech machinery and equipment manufacturers are recognized for their precision, reliability, and innovation. The sector produces a wide range of products, including machine tools, industrial machinery, mining equipment, agricultural machinery, and more. Czech machinery companies are known for their competitiveness and export orientation, catering to both domestic and international markets.
Electrical engineering is another prominent industry in the Czech Republic. The sector covers the production of electrical machinery, appliances, and electronic components. Czech companies excel in various sub-sectors, including power generation equipment, electrical motors, transformers, electronic devices, and telecommunications equipment. The country has a skilled workforce and a supportive research and development environment, fostering technological advancements in the electrical engineering sector.
The chemical industry also plays a significant role in the Czech industrial landscape. The country has a well-established chemical sector that produces a wide range of chemicals, including plastics, rubber, pharmaceuticals, fertilizers, and specialty chemicals. The chemical industry benefits from the country's strategic location and well-developed transportation infrastructure, enabling efficient supply chain management and access to international markets. Czech chemical companies are known for their high-quality products, research and development capabilities, and adherence to environmental standards.
Food processing is an essential industry in the Czech Republic, contributing to both domestic consumption and exports. The country has a strong agricultural base, and food processing companies specialize in meat products, dairy products, confectionery, beverages, and more. Czech food producers emphasize quality, tradition, and innovation, catering to the preferences of domestic and international consumers. The industry is supported by stringent food safety regulations and a commitment to sustainable production practices.
The Czech Republic has also witnessed the growth of the information technology and software development industry. The country has a well-educated and skilled workforce in the field of information technology. Czech IT companies provide a wide range of services, including software development, IT consulting, system integration, and outsourcing. The sector benefits from a favorable business environment, innovation hubs, and government support for research and development.
The Czech industrial sector has benefitted from the country's strategic location within Europe, a well-developed infrastructure, a skilled workforce, and a business-friendly environment. The government has implemented policies to attract foreign investment, support research and development, and foster innovation. The industrial sector's export orientation has been crucial for the Czech economy, as it has allowed the country to tap into global markets and contribute to a positive trade balance.
However, challenges exist within the Czech industry. These include the need to continuously invest in research and development, embrace digitalization and Industry 4.0 technologies, and address environmental sustainability. Additionally, maintaining a skilled workforce, supporting small and medium-sized enterprises, and fostering innovation and collaboration between the industry and academia are important areas for further development.
In summary, the Czech industrial sector is diverse and well-developed, encompassing automotive manufacturing, machinery, electrical engineering, chemicals, food processing, and more. The sector's competitiveness, export orientation, and innovation have been vital for the country's economic growth and integration into global markets. Continued focus on technological advancements, sustainability, and collaboration will be essential for the industry's future success. |
| Military |
| History: |
The Czech Republic maintains a unified armed forces structure comprising the Czech Army, the Czech Air Force, and other supporting branches. The primary objective of the armed forces is to ensure the sovereignty, territorial integrity, and security of the Czech Republic, as well as contribute to international peace and stability.
The Czech Army is responsible for land-based operations and defense. It consists of combat and support units that are trained and equipped to fulfill various military roles. The army possesses a range of capabilities, including infantry, armored and mechanized units, artillery, engineers, and special forces. The army's structure is adaptable and capable of participating in a wide range of missions, from territorial defense to international peacekeeping and humanitarian operations.
The Czech Air Force is tasked with air defense, aerial operations, and support for ground forces. It operates a fleet of modern aircraft, including multi-role fighters, transport aircraft, helicopters, and unmanned aerial systems. The air force's capabilities enable it to conduct air superiority missions, close air support, aerial reconnaissance, and transportation of personnel and equipment. The Czech Air Force also participates in international air policing missions, contributing to the collective defense of NATO airspace.
The armed forces of the Czech Republic are actively engaged in international cooperation and contribute to various multinational operations. As a NATO member, the Czech military participates in alliance-wide initiatives, joint exercises, and deployments alongside other member states. The armed forces have also participated in international missions authorized by the United Nations and other international organizations. These missions have included peacekeeping, stabilization efforts, and humanitarian assistance in regions such as Afghanistan, the Balkans, and Africa.
The Czech Republic is committed to maintaining a capable and technologically advanced military force. It invests in defense modernization, including the procurement of new equipment, upgrading existing systems, and enhancing interoperability with NATO allies. The armed forces prioritize training and professional development to ensure personnel readiness and effectiveness. Additionally, the Czech Republic maintains a robust defense industry, which contributes to domestic defense capabilities and fosters technological innovation.
Civil-military cooperation is an integral part of the Czech armed forces' activities. The military collaborates with civilian authorities, including the Ministry of Defense, the Ministry of the Interior, and other relevant agencies, to enhance overall security and crisis response capabilities. This cooperation extends to disaster response, border security, and counterterrorism efforts. The armed forces also engage in public outreach programs to promote awareness, understanding, and support for their mission and activities among the general public.
The Czech Republic is committed to meeting its NATO defense spending targets and maintaining a sustainable defense budget. This ensures the armed forces have the necessary resources to fulfill their roles effectively. The government also recognizes the importance of investing in defense research and development to stay at the forefront of emerging technologies and maintain a technologically advanced force.
Challenges facing the Czech armed forces include addressing evolving security threats, such as cyber warfare, terrorism, and hybrid warfare tactics. The military must continually adapt its capabilities, doctrine, and training to counter these challenges effectively. Recruitment and retention of qualified personnel, maintaining high operational readiness, and ensuring the welfare and well-being of military personnel are ongoing priorities.
In summary, the armed forces of the Czech Republic are a professional and modern military organization committed to the defense and security of the country. The Czech Army and Air Force, supported by other branches, possess the capabilities to fulfill a range of military missions and contribute to international security efforts. Collaboration with NATO allies, investment in modernization, and cooperation with civilian authorities are essential elements of the Czech armed forces' activities. |
| Soldiers: |
0 |
| Tanks: |
0 |
| Aircraft: |
0 |
| Ships: |
0 |
| Missiles: |
0 |
| Nuclear Weapons: |
0 |
| Last Updated: 08/03/2023 10:30 am |